Type One Error and Type Two Errors are the two mistakes we can make. The amount of emergency department visits is not related to the amount of stress an individual has Describe type 1 and type 2 errors that could result from this null hypothesis.
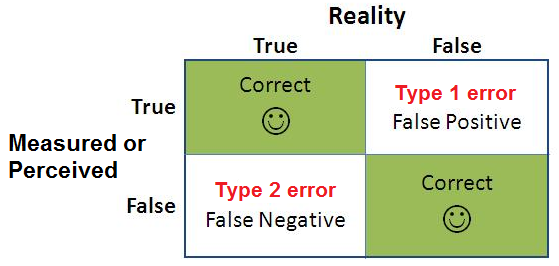
What Are Type 1 And Type 2 Errors
3 rows Type I and Type II errors are subjected to the result of the null hypothesis.
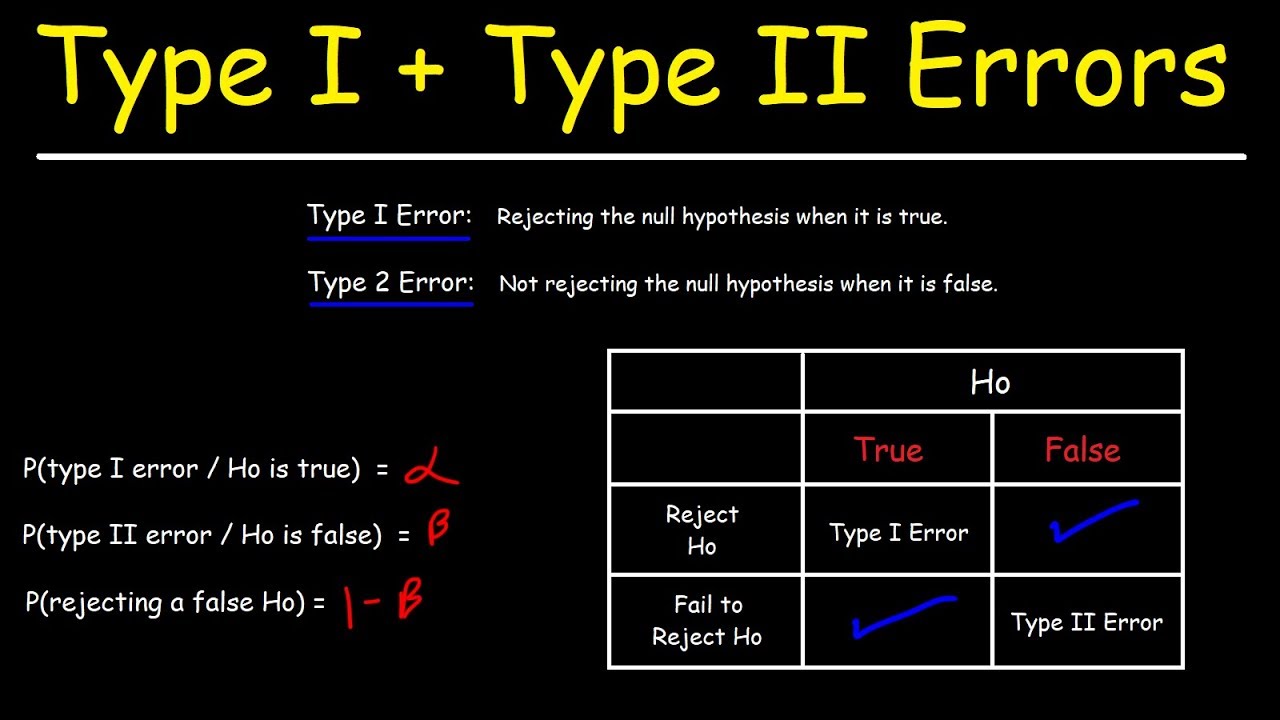
. The USDA limit for salmonella contamination for chicken is 20. Understanding Type I and Type II Errors Hypothesis testing is the art of testing if variation between two sample distributions can just be explained through random chance or not. 1 Type 2 2 Type 1.
Random chance and improper research techniques. We conclude that the proportion of high school seniors who get drunk each month is not 29 when it really is 29. Type II errors typically lead to the preservation of the status quo ie.
And well do this on some population in question. The power of the test can be P R H is truea. Type II error in a test with rejection region R is 1 is true P R H a.
In a Type 2 error you fail to reject a null hypothesis when it is false. We review their content and use your feedback to. Once the level of significance is set the probability of a type 2 error failing to reject a false null hypothesis can be minimized either by picking a larger sample size or by.
Other Apps - April 14 2022 What Are Type 1 And Type 2 Errors How To Identify Type I And Type Ii Errors In Statistics Youtube What Are Type 1 And Type 2 Errors Type I Type Ii Errors Differences Examples Visualizations. What causes type 1 errors. Describe type 1 and type 2 errors that could result from this null hypothesis.
No random sample whether its a pre-election poll or an AB test can ever perfectly represent the population it intends to describeSince researchers sample a small portion of the total population its possible that the results dont accurately. The probability of a type 1 error rejecting a true null hypothesis can be minimized by picking a smaller level of significance α before doing a test requiring a smaller p -value for rejecting H 0. Develop analytical superpowers by learning how to use programming and data analytics tools such as VBA Python Tableau Power BI Power Query and more.
If Sams test incurs a type I error the results of the test will indicate that the difference in the average price changes between large-cap and small-cap stocks exists while there is no significant difference among the groups. Interventions remain the same when change is needed. A Type I error means that you would send an innocent man or woman to jail.
Accuracy is the most important element in psychology therefore we only accept a result when there is 95 confidence in the effect and only 5 chance results could occur if there was no effect. - Instructor What were gonna do in this video is talk about Type I errors and Type II errors and this is in the context of significance testing. At the same time a Type II error is not exactly ideal either as it.
Decrease the significance level alpha level Type 2 error is believing that the null hypothesis is correct when it is not. Limit the chances of type 1 error. A meat inspector reports that the chicken produced by a company exceeds the USDA limit.
The professor does not buy the software but in reality it would have decreased the dropout rate. You reject the null hypothesis that there is no difference in mean height between these two populations. So just as a little bit of review in order to do a significance test we first come up with a null and an alternative hypothesis.
We do not reject that the mean starting salary is at least 100000 when in fact it is less than 100000. Who are the experts. The professor buys the software but the dropout rate does not change.
Limit the chances of type 2 error. Twenty-nine percent of high school seniors get drunk each month. If he is convicted for something he has not done a type 1 error has occurred.
If we have to conclude that two. The consequences of making a type I error mean that changes or interventions are made which are unnecessary and thus waste time resources etc. Type II errors happen when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis.
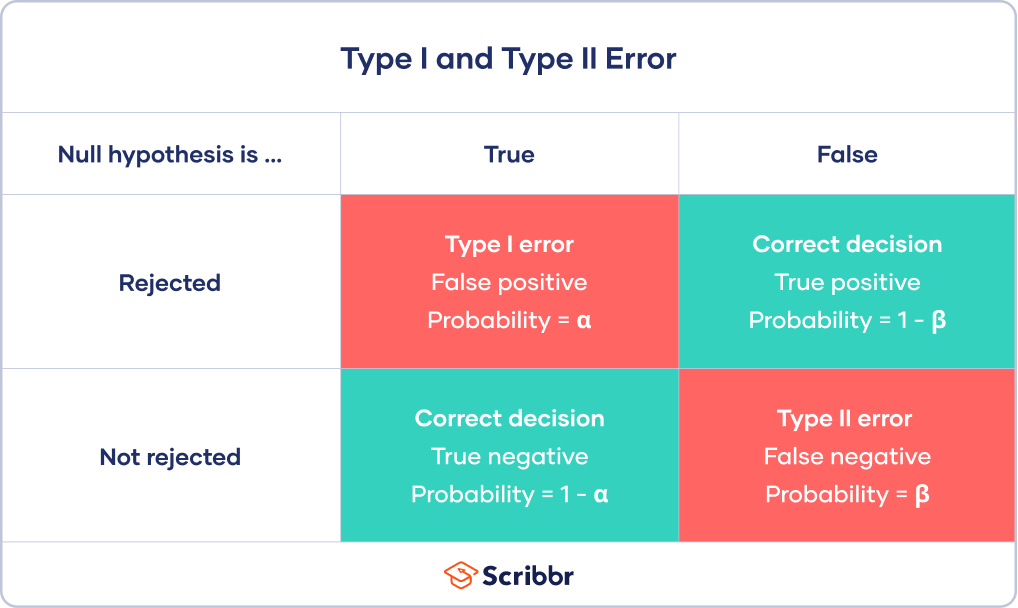
A type II error false-negative occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Type 1 errors can result from two sources.
Describe Type 1 and Type 2 Errors Get link. In reality there is no difference but something about the way you drew the samples or perhaps even the size of the samples has caused you to commit a Type 1 error. This problem has been solved.
Briefly describe type 1 and type 2. Consider the following null hypothesis. However even if were 95 confident there is still a chance we can get it wrong.
Summary of Type 1 and Type 2 Errors Type 1 error is believing that the alternative hypothesis is correct when it is not. A Type One Error is. A type I error false-positive occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population.
Type I errors happen when we reject a true null hypothesis. Briefly describe type 1 and type 2 errors. In case of type.
Type I or Type II. Suppose the null hypothesis is that the dropout rate is 13 and the alternative is p.

How To Identify Type I And Type Ii Errors In Statistics Youtube
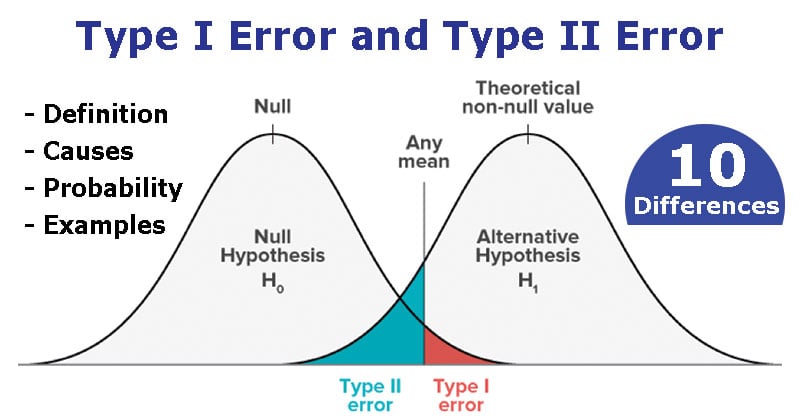
Type I Error And Type Ii Error Definition 10 Differences Examples Microbe Notes
0 Comments